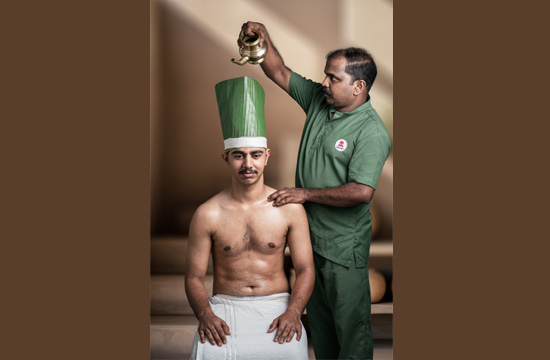
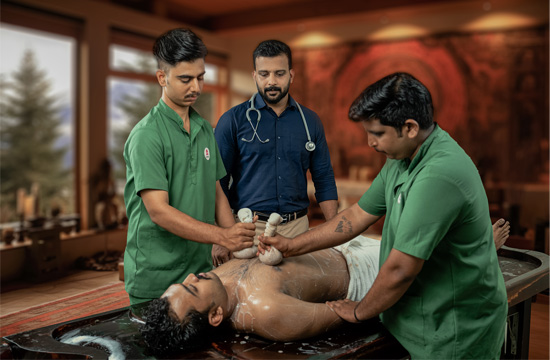
Steam Bath
A steam bath, also known as Swedana in Ayurveda, is a therapeutic procedure that involves exposing the body to steam generated from boiling water infused with medicinal herbs. This treatment is designed to open the pores, promote sweating, and help eliminate toxins from the body. It is an integral part of the Panchakarma detoxification process in Ayurveda and is often used in conjunction with other treatments.
Overview
A steam bath is a simple yet powerful therapeutic practice used in Ayurveda for its various health benefits. It is beneficial for improving circulation, detoxifying the body, relieving muscle tension, and enhancing overall well-being.
Procedure
- Preparation:
- The patient is usually given an oil massage (Abhyanga) before the steam bath. This helps in loosening the toxins and prepares the body for the detoxification process.
- The herbal steam is generated by boiling water with medicinal herbs selected based on the individual’s health condition and treatment goals.
- Steam Exposure:
- The patient sits or lies in a special steam chamber or steam tent that exposes the body to steam while keeping the head outside to avoid overheating and ensure comfortable breathing.
- The steam session typically lasts for about 10 to 20 minutes, or until the patient begins to sweat profusely.
- The warmth and humidity from the steam cause the body to sweat, helping in the elimination of toxins through the skin.
- Post-Treatment Care:
- After the steam bath, the patient is usually advised to rest for a short period and avoid exposure to cold air or wind.
- Hydration is important, so drinking warm water or herbal tea is recommended to replenish fluids lost during sweating.
- The patient may also take a warm shower to rinse off the sweat and residual oil.
Indications
A steam bath is beneficial for a variety of health conditions and is indicated for:
- Detoxification: Helps in the elimination of toxins from the body.
- Respiratory Issues: Useful for conditions like asthma, bronchitis, and sinusitis as it helps clear the respiratory passages.
- Muscle and Joint Pain: Relieves muscle tension, stiffness, and joint pain.
- Skin Health: Opens up pores, enhances blood circulation, and promotes healthy, glowing skin.
- Weight Management: Assists in weight loss by promoting sweating and increasing metabolism.
- Stress and Fatigue: Provides relaxation and helps reduce stress and fatigue.
Benefits
- Detoxification: Promotes the removal of toxins through sweat.
- Improved Circulation: Enhances blood circulation, bringing more oxygen and nutrients to tissues.
- Pain Relief: Alleviates muscle and joint pain, and reduces stiffness.
- Skin Rejuvenation: Cleanses the skin, opens pores, and promotes a healthy complexion.
- Relaxation: Induces relaxation, reduces stress, and helps in better sleep.
Contraindications
A steam bath may not be suitable for:
- Individuals with heart conditions or high blood pressure.
- Pregnant women.
- Patients with acute infections or fever.
- People with severe skin conditions or open wounds.
- Those who are severely dehydrated or have certain respiratory conditions.
Santhigiri Ayurveda & Siddha Hospital
Steam Bath at Santhigiri
At Santhigiri Ayurveda & Siddha Hospital, steam baths are an integral part of the therapeutic regimen. The hospital ensures that steam baths are administered under the supervision of experienced practitioners. The use of high-quality herbal infusions and a serene environment enhances the therapeutic benefits of the treatment. Each session is tailored to meet the specific health needs of the patient, ensuring a holistic approach to wellness and detoxification.
Conclusion
A steam bath is a powerful Ayurvedic treatment that offers numerous health benefits, including detoxification, improved circulation, pain relief, and relaxation. When administered at Santhigiri Ayurveda & Siddha Hospital, the treatment is carried out with precision and care, ensuring maximum therapeutic benefits. This traditional practice continues to be an effective method for promoting overall health and well-being.